Google is making significant strides in the world of artificial intelligence with the latest global update to its Bard chatbot. Bard, now powered by the Gemini Pro model, is poised to revolutionize conversational AI with support for more than 40 languages, including Arabic, Chinese, Dutch, French, German, Hindi, Japanese, Portuguese, Spanish, Tamil, Telugu, and Malayalam.
The journey towards this milestone began in December when Google introduced its new generation of AI models, comprising the flagship Gemini Ultra, the streamlined Gemini Pro, and the compact Gemini Nano, specifically designed for devices like the Pixel 8. At that time, Bard received an initial boost with the Gemini Pro update, initially for English conversations.
While the precise improvements achieved with Gemini Pro weren’t quantified, Google assured that Bard’s capabilities have been significantly enhanced. These enhancements encompass a wide array of AI-driven tasks, including content comprehension, summarization, reasoning, brainstorming, writing, and planning. The goal was to create a more intuitive and capable conversational AI experience for users.
Bard itself has undergone a series of transformations behind the scenes. It made its debut in February 2023, initially powered by LaMDA (Language Model for Dialogue Applications). Subsequently, it received an update in the form of PaLM 2 later in the same year. Now, with the integration of Gemini Pro, Bard’s reach extends to more than 230 countries, marking a global expansion of its capabilities. Admittedly, the nomenclature of these models and versions can be a tad bewildering.
One notable feature introduced in September is the “Double check” function, which leverages Google Search to cross-reference Bard-generated results. Initially available in English, this feature has now been extended to support more than 40 languages, further enhancing its utility.
In a noteworthy development, Google is introducing image generation support through the Imagen 2 model. However, this feature is currently available exclusively in English. Users can harness this capability by typing image-related queries directly into the chatbot interface. For instance, typing “create an image of a futuristic car” prompts Bard to generate a visual representation of the request.
To ensure the authenticity of images produced by Bard, Google has incorporated a SynthID digital watermark, a technology developed by DeepMind. This watermark is embedded in the pixels of the generated images, although identifying it requires the use of Google’s proprietary tools.
Beyond text-based interactions, Google has integrated Bard’s AI capabilities into Google Assistant. This enables users to perform a wide range of tasks, such as trip planning and creating grocery lists. To maintain a safe and responsible environment, certain restrictions are in place to prevent Bard from generating content that may be deemed unsafe, particularly for teenagers.
Prerequisites for accessing Google Gemini Pro
Before embarking on your journey to interact with Google’s powerful Gemini AI assistant, there are certain prerequisites that need to be met. Here’s a breakdown of the requirements to gain access to this cutting-edge service:
- Google Account: To begin your Gemini AI experience, you’ll need a Google account. This applies to both free and paid Google accounts, ensuring accessibility for a wide range of users.
- Access Permissions: Accessing Google Gemini requires authorized permissions within your Google account. This process is seamlessly handled if you receive an invitation, making it hassle-free for invited users.
- Hardware Device Access: For engaging in meaningful conversations with Gemini, you’ll need compatible devices that support Google apps and services. Whether you’re using a smartphone, tablet, or laptop, as long as it’s equipped with internet connectivity, you’re all set.
- App/Browser Access: Google offers access to Gemini AI through various channels. You can utilize dedicated apps like Google Search and Assistant, or access it through dedicated websites, which are fully functional on modern internet browsers.
- Usage Quotas: Depending on your access type, whether it’s free or paid, there might be usage quotas in place. These quotas can be measured in terms of conversation time or the number of queries you make. Be aware of your usage limits to make the most of this service.
As long as you have a compatible device and an active Google account with authorized Gemini access, you’re ready to dive into the world of interactions with this AI assistant.
Modes of interaction with Google Gemini Pro
Google has gone the extra mile to offer multiple avenues for interacting with its versatile Gemini AI, accommodating both text and voice-based interactions. Here’s an overview of the diverse modes of engagement:
- Web Chat Interface: The most straightforward method is through a dedicated website equipped with an AI chatbot interface that facilitates text-based conversations. It’s a user-friendly way to engage with Gemini.
- Google Search Integration: Gemini seamlessly integrates with Google Search, allowing it to provide interactive and conversational responses to your search queries. This integration enables smooth follow-up interactions.
- Google Assistant Integration: If you prefer voice-based interactions, you’re in luck. Gemini can be accessed through Google Assistant on your mobile devices or smart speakers. Simply speak your queries, and Gemini will respond with the utmost accuracy.
- Custom App Integration: For a tailored experience, Gemini’s capabilities can be integrated into third-party applications through APIs. This opens up opportunities to create customized conversational experiences to meet specific needs.
Google’s Bard surpasses GPT-4 in chatbot rankings
In a dramatic turn of events, Google’s Bard, fueled by the potent Gemini Pro update, has risen above OpenAI’s GPT-4 and Claude, heralding a remarkable shift in the ever-evolving chatbot landscape.
- Google’s Bard ascends to the second-highest position on the LMSYS Chatbot Arena Leaderboard, overtaking OpenAI’s GPT-4.
- This momentous feat challenges the dominance of OpenAI’s leading chatbot models.
- Bard is in hot pursuit of GPT-4 Turbo, the reigning champion, and GPT-4, both of which have maintained their stronghold on the top two spots for an extended period.
- Bard’s meteoric rise can be attributed to its integration with Google’s groundbreaking Gemini Pro large multimodal model.
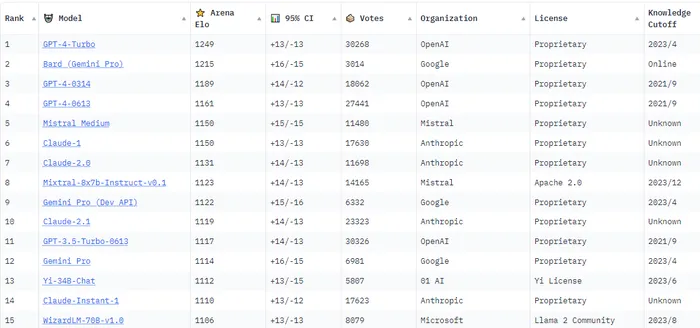
The Chatbot Arena Leaderboard is the brainchild of LMSYS Org (Large Model Systems Organization), a collaborative research group founded by the University of California, Berkeley, in collaboration with the University of California, San Diego, and Carnegie Mellon University. The organization, responsible for creating Vicuna LLM, hailed Bard’s ascent as a “remarkable achievement.”
The Chatbot Arena serves as a benchmark platform for evaluating large language models through anonymous, randomized battles conducted in a crowdsourced manner. Rankings are determined using the Elo rating system, a widely recognized methodology employed in competitive games like chess.
Bard’s exceptional performance powered by Gemini Pro places it as only the second model on the leaderboard to achieve a score surpassing 1200.
Bard’s meteoric rise coincides with Google’s ongoing efforts to enhance the underlying models that drive this chatbot. PaLM 2 has been replaced by Gemini, Google’s most formidable model to date. The unveiling of Gemini last December introduced the initial Pro version for Bard, with the colossal Gemini Ultra set to make its debut in the near future.
Additionally, Bard outshone all iterations of Claude, with the Gemini Pro Dev API version securing a higher rank than Anthropic’s Claude 2.1 and GPT 3.5 Turbo. The excitement in the chatbot community is palpable, with speculations on what the future holds for Bard and the impending release of Gemini Ultra.
This surge in the leaderboard is a welcome development for Google, especially considering Bard’s initial challenges. However, Bard has since received routine updates, expanding its integration into various Google apps, including YouTube and Docs.
OpenAI’s GPT-4 has consistently occupied the top spot on model leaderboards, maintaining its supremacy on Stanford’s HELM Leaderboard, with GPT-4 Turbo securing second place.
Google Bard: a significant help to support your internationalization process
Google Bard’s global expansion and multilingual capabilities make it an invaluable tool for companies looking to streamline their internationalization efforts. With support for over 40 languages and its ability to understand, summarize, and generate content in various tongues, Bard simplifies cross-border communication and content creation. Additionally, its image generation feature can aid in creating culturally relevant visuals, further enhancing marketing and localization strategies. By harnessing the power of Google Bard, businesses can effectively connect with diverse audiences worldwide, fostering growth and success in the global market.
Integrating Google Bard into various aspects of a company’s operations can significantly enhance its competitiveness on a global scale. For instance, when integrated into customer support processes, Bard can provide multilingual assistance around the clock, improving customer satisfaction and retention. This responsiveness can set a company apart from competitors and bolster its global reputation. Furthermore, Bard’s language capabilities extend to market research, enabling businesses to analyze and understand international trends, giving them a strategic edge in product development and marketing campaigns. Overall, the seamless integration of Google Bard empowers companies to operate more efficiently and effectively on a global stage, ultimately driving success and growth.
In summary, Google’s latest update to Bard, powered by the Gemini Pro model, represents a significant leap forward in the world of AI-driven conversational agents. With support for numerous languages, image generation capabilities, and integration into Google Assistant, Bard is poised to play a pivotal role in enhancing user experiences across various domains, from casual conversations to practical tasks.
